What is dysautonomia?
The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is the part of the nervous system that regulates functions that are automatic in nature such as heart rate, blood pressure, digestion, excretion, perspiration, temperature regulation, pupil dilation, circulation, and respiration among others.
The ANS is responsible for maintaining homeostasis, or equilibrium, in the body. When there is a dysfunction or failure of the autonomic nervous system, the result is a disorder classified as a type of dysautonomia. Dysautonomia is not a diagnosis. It’s an umbrella term to describe autonomic disorders. It’s sometimes referred to as autonomic dysfunction or autonomic neuropathy.
It is estimated that 70 million people worldwide have some form of autonomic dysfunction. Often dysautonomias are invisible illnesses. Patients may not look sick, and yet they have symptoms that make it difficult to work, go to school, and perform activities of daily living.
Common Symptoms
The symptoms experienced by dysautonomia patients vary based on the type of autonomic dysfunction and where the dysfunction is occurring within the body.
Here are the seven most common symptoms:
- Difficulty Standing Still
- Fatigue
- Lightheadedness
- Nausea and Other GI Symptoms
- Brain Fog and Mental Clouding
- Palpitations or Chest Discomfort
- Shortness of Breath or Difficulty Breathing
Dysautonomia symptoms are not limited to these seven. The organ systems most commonly affected in dysautonomias are neurological, pulmonary, cardiovascular, urinary, gastrointestinal, secretomotor and pupillomotor. Because autonomic disorders affect multiple organ systems, the presentation of symptoms are heterogenous, widely varying between different individuals. For example, one patient with POTS (a common autonomic disorder) may have the chief complaint of abdominal pain while the next POTS patient identifies migraine headaches as their primary symptom.
Orthostatic Intolerance

One common sign of autonomic dysfunction is difficulty maintaining upright posture. This is known as orthostatic intolerance and involves abnormal blood pressure and heart rate. Patients with orthostatic intolerance present with feelings of lightheadedness, dizziness, and brain fog. It’s caused by a loss of blood flow to the brain, heart, and lungs. This is not a life-threatening decrease in blood flow, but it’s bothersome and some cases causes fainting.
Another symptom of orthostatic intolerance or orthostatic hypotension when standing upright is an annoying pain in the back of the neck and shoulders. This is not always a symptom nor a primary symptom. Because of the distribution of the discomfort, this is sometimes referred to as the “coat hanger sign” which occurs as pain in the back of the neck when standing. The exact mechanism of the coat hanger phenomenon is unknown, but one theory suggests it is a kind of cramp caused when the antigravity muscles holding up the head receive too little blood flow.
The following graphic depicts common symptoms and the organ systems affected.
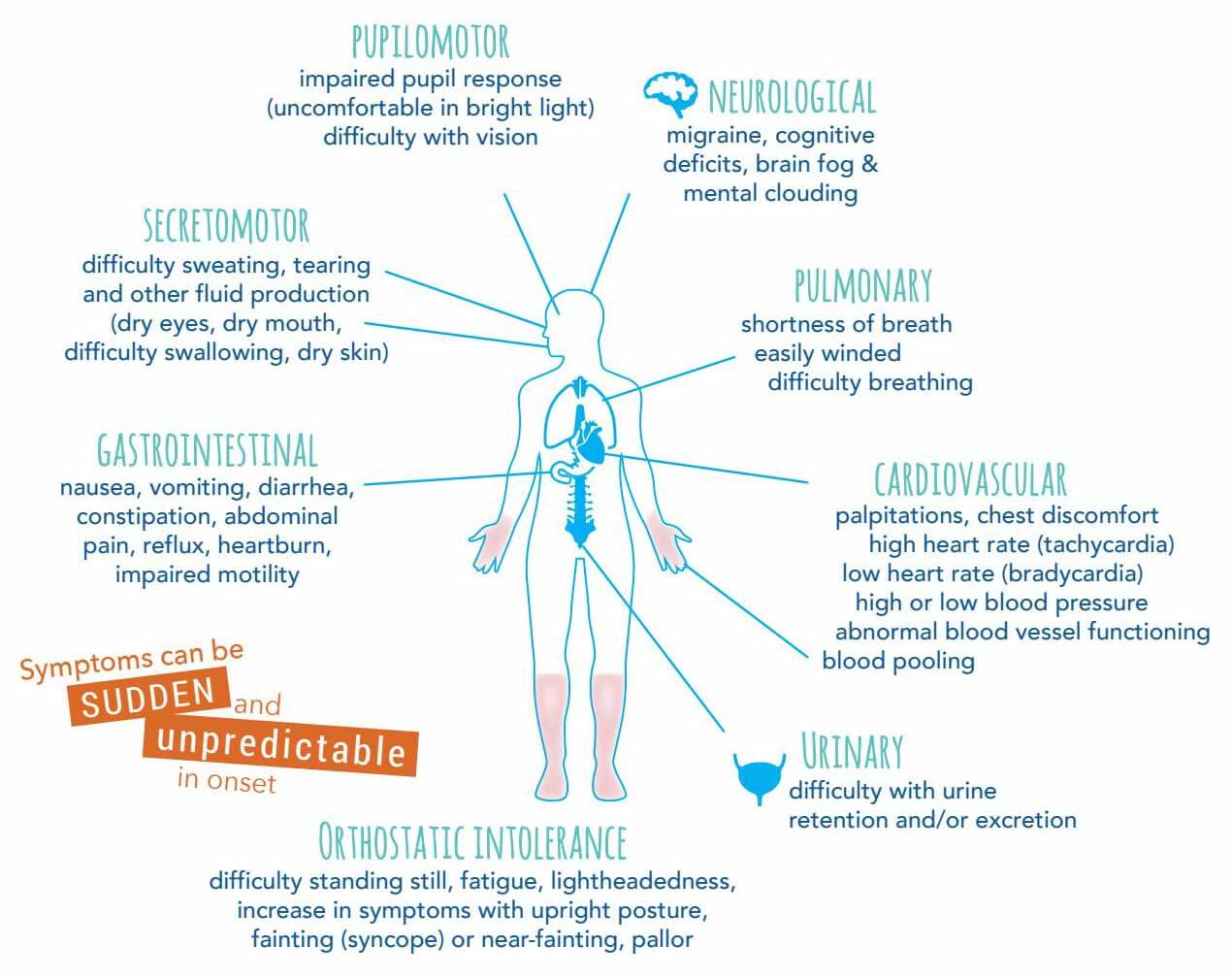
Pupilomotor Symptoms: impaired pupil response (uncomfortable in bright light) and impaired vision.
Neurological Symptoms: migraines, cognitive deficits, brain fog and mental clouding.
Pulmonary Symptoms: shortness of breath, easily winded, and difficulty breathing.
Cardiovascular Symptoms: palpitations, chest discomfort, high heart rate (tachycardia), low heart rate (bradycardia), high or low blood pressure, abnormal blood pressure functioning, and blood pooling.
Urinary Symptoms: difficulty with urine retention and/or excretion.
Gastrointestinal Symptoms: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, abdominal pain, reflux, heartburn, and impaired motility
Secretomotor Symptoms: difficulty sweating, tearing, and other fluid production (dry eyes, dry mouth, difficulty swallowing, dry skin).
Orthostatic Intolerance Symptoms: difficulty standing still, fatigue, lightheadedness, increase in symptoms with upright posture, fainting (syncope) or near-fainting, and pallor.
Symptoms can be triggered by dehydration, tight clothing, hot environments, stress, and alcohol consumption.
Again, this is not an exhaustive list of symptoms. Any symptom in any organ system could potentially be the result of an autonomic disorder. Understanding which symptoms affect you the most is important when identifying treatments with your doctor. Once you’ve been diagnosed with an autonomic disorder, every future or co-existing condition needs to be considered in light of your diagnosis and considered as potentially being caused by the autonomic disorder.
Types of Dysautonomia
There are at least 15 distinct dysautonomias. The most common are postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS) and neurocardiogenic syncope/autonomic mediated syncope.
Autonomic dysfunction can occur at any age: pediatric, adult, or geriatric. It can range from mild to disabling and may or may not be neurodegenerative. Because there are many forms of dysautonomia, we use the singular term “dysautonomia” to reference autonomic disorders in general or when referring to a specific condition such as “orthostatic hypotension.” We use “dysautonomias” when referring to many disorders of the autonomic nervous system.
Age and Onset of Dysautonomias
Pediatric Onset (very rare)
Also known as genetic or hereditary dysautonomias, these conditions often reflect problems or mutations which occur during the development of the autonomic nervous system. One type of mutation, found almost exclusively in people of Ashkenazi Jewish heritage, affects the autonomic and sensory nervous system development causing familial dysautonomia (FD)
Another mutation causes an increased level of phenylalanine (Phe) in the bloodstream resulting in a metabolic disorder called phenylketonuria (PKU). Another mutation in the ATP7A gene that is responsible for transporting copper throughout the body causes “kinky hair” and is known as Menkes disease. In Hirschsprung’s disease there is a lack of development of nerve cells in the enteric nervous system. It’s important to note that, in general, dysautonomias in early childhood are rare. For more information: Pediatric Dysautonomias.
Other pediatric autonomic disorders include:
Hereditary Sensory and Autonomic Neuropathy (HSAN)
Congenital Central Hypoventilation Syndrome (CCHS)
Catecholaminergic Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia (CPVT)
Teen/Adult Onset
In teens and adults, autonomic dysfunction usually reflects functional changes in a generally intact autonomic nervous system. It is estimated that postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS), a common autonomic disorder, affects 1 out of every 100 teens. Dysautonomias in adults often are associated with, and may be secondary to, another disease process or a drug. Common secondary causes include medications, chemotherapy, radiation treatments, spinal cord or head injury, or diabetes (such as diabetic autonomic neuropathy). Less commonly, the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks and damages certain parts of the autonomic nervous system in autoimmune autonomic ganglionopathy.
Autonomically mediated syncope, also called vasovagal syncope, neurally mediated syncope or neurocardiogenic syncope, is another example of teen/adult dysautonomia. Individuals with autonomically mediated syncope suffer from frequent episodes of fainting or near fainting where the blood pressure drops by 20 mmHg systolic/ 10 mmHg diastolic with upright posture. Most patients have symptoms with little change in heart rate. In some cases, the drop in blood pressure occurs as a compensatory function following tachycardia, as seen in POTS, or bradycardia can precede a drop in blood pressure. For more information: Teen and Adult Onset of Dysautonomia.
The most common form of dysautonomia is Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS).
Dysautonomias Ages 50+
Any autonomic disorder diagnosis after the age of 50 is considered geriatric onset. In these patients, dysautonomia typically reflects a neurodegenerative disease. The degeneration may be in the form of lesions in the central nervous system, as in multiple system atrophy (MSA), or in loss of autonomic nerves not involving the central nervous system, as in pure autonomic failure (PAF). Most geriatric cases involve damage to nerves that result in loss of autonomic reflexes, also known as autonomic failure. It is common in geriatric patients to experience some orthostatic hypotension which is characterized by a drop in blood pressure upon standing.
Neurogenic orthostatic hypotension is a neurodegenerative form of dysautonomia in which the autonomic system loses the ability to properly regulate blood pressure as one moves from sitting or lying down to standing. Evidence suggests that the autonomic nervous system (ANS) is affected by dementia. In many types of dementia, neuropathological lesions can be found in the ANS. Lewy body disorders (LBD), which include Parkinson’s disease (PD) and dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB), commonly involve ANS dysfunction.
For more information: Dysautonomias Ages 50+
Primary, Secondary or Idiopathic
Regardless of when an autonomic dysfunction occurs in life, these disorders can be primary, secondary, or idiopathic. A primary dysautonomia is when we know autonomic dysfunction is the main disease process. Examples of primary dysautonomias include familial dysautonomia, multiple system atrophy, pure autonomic failure, and some forms of syncope among others.
Secondary dysautonomias are experienced because of another disease process, as in autonomic neuropathy associated with diabetes or POTS resulting from an autoimmune disease.
Conditions in which secondary dysautonomia might occur:
Amyloidosis
Celiac disease
Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease
Chiari malformation
Crohn’s disease
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
Ulcerative Colitis
Guillain-Barre syndrome
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
Lambert-Eaton syndrome
Lupus
Lyme disease
Muscular sclerosis
Parkinson’s
Rheumatoid arthritis
Sarcoidosis
Sjogren’s syndrome
Vitamin B and E deficiencies
Diabetes
Idiopathic dysautonomias are autonomic nervous system disorders where the main disease process is unknown. The pathophysiology of most autonomic disorders is complex and not well known, therefore it is helpful to discuss with your doctor if your dysautonomia is a primary, secondary, or idiopathic disorder. You may not be able to get to the root of your dysautonomia, but the process of trying to identify the cause may help with symptom treatment and management.
Coexisting Conditions and Autonomic Symptoms
Since dysautonomia patients experience many symptoms from multiple organ systems, it is helpful to consider the possibility of underlying causes or coexisting conditions.

Common coexisting conditions associated with autonomic disorders:
Diagnosing Dysautonomias
Clinical Assessment: A doctor who understands dysautonomia should conduct a clinical assessment which includes a comprehensive medical history and physical examination.
Orthostatic Vitals Test: This test can be performed in a doctor’s office by a nurse or properly trained staff member. The test results may provide meaningful data about the patient’s response to orthostatic stress. More importantly, an orthostatic vitals test may confirm a suspected dysautonomia without the use of expensive diagnostic testing.
Tilt Table Test: This test is done to see how the body reacts to changes in position, specifically if standing up (orthostasis) provokes orthostatic hypotension, neurally mediated hypotension, an excessive increase in pulse rate, or autonomically mediates syncope. The tilt table test used to be considered the “gold standard” in testing for dysautonomias. Today, most clinicians are comfortable confirming an autonomic disorder with orthostatic vitals testing.
Other tests available at many major autonomic laboratories include:
Quantitative Sudomotor Axon Reflex Test (QSART)
The Valsalva Maneuver
The Cold Pressor Test
Heart Rate Variability
Blood Volume Testing
Catecholamine Tests
Antibody Test
Skin Biopsies
For more information on clinical autonomic testing see our course Introduction to Clinical Autonomic Testing.

Treating Dysautonomia
There is no known cure for autonomic disorders, but the symptoms can be managed. Any treatment should be done while under the care of a provider who understands dysautonomias. Some of the treatments used for common symptoms include:
- Increasing water intake by 2-3 liters of fluid daily to keep your blood volume up. Discuss the amount of fluid intake with your provider.
- Adding sodium (salt) to your daily intake. Salt helps to retain fluid volume in your blood vessels which helps with blood pressure. In most cases, 5-9 grams of salt daily. Discuss with your provider.
- Exercise
Non-Pharmacological Treatments
Several non-pharmacological treatments are used to help patients with autonomic disorders. Although these treatments do not involve medicine, patients should discuss the use of such therapies with their provider as a part of their treatment plan.
Top 10 Non-Pharmacological Treatments
Several drug treatments are used for managing the symptoms of autonomic disorders. Most of these medications are not FDA approved for the use of treating dysautonomias but are used “off-label.” Each of these has been successfully used in treating some patients. Since these medications can produce harmful side effects, patients should take medications only under the supervision of a provider with expertise in the treatment of dysautonomias.
Top 20 Dysautonomia Drugs
Alternative Treatments
TDP strives to bridge the gap between what the top autonomic specialists in the world know and what community providers and patients need to know. TDP is committed to sharing accurate, science-based information and working with the American Autonomic Society (AAS) to make sure our message is scientifically valid, and it gets into the hands of those who need it most. However, we also recognize that some patients access alternative treatments that offer relief from their symptoms. It’s recommended that you talk with your provider about any course of treatment you pursue. Some of these alternative treatments include:
- Acupuncture
- Cranio-sacral massage therapy
- Chiropractor
- Yoga
- Massage therapy
- Eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR)
- Tap and sound therapy
- Reflexology
- Bemer therapy
- IV therapy
- Hyperbaric oxygen change
- Deep breathing exercises
- Dry brushing
- Alternative diets: You may consider an organic, whole foods approach that reduces sugar, certain carbohydrates, and artificial/processed foods. Gluten and dairy free diets may help some people.
Prognosis
No two dysautonomia patients look the same. Dysautonomia can be mild or debilitating. A more severe case will require significant lifestyle changes as you try different treatments to address symptoms. For some patients, the goal is to have more good days than bad. Symptom management is possible, but it takes time and patience. Because the autonomic nervous system adapts and changes, the course of your condition may change as well. Some patients find a treatment plan that works for a while, but then a new symptom appears and becomes their chief complaint. This is why finding a provider who understands dysautonomia and can help you manage your individual case is so important. It’s also why patients must become their own advocate and participate in the process of managing their symptoms. This includes partnering with your doctor by tracking symptoms, responses to treatment, and providing this data at your appointments.
Practical Tips for Living with Dysautonomia
- Energy drinks and alcohol should be consumed with caution or avoided. Both are dehydrating in nature and can affect the heart and nervous system. Carbonated beverages should be ingested sparingly, or not at all, as the body must work to expel the extra ingested carbon dioxide.
- Eat smaller meals to aid digestion
- Avoid standing or sitting for long periods of time. If you feel dizzy, sit down, lie down, and raise your feet.
- Avoid heat. This includes hot showers.
- Get enough sleep. Establish an evening routine and try to stick to it. This is especially important for teens with POTS.
- Manage stress
- Ask for help when you need it
- Pay attention to your mental health and ask for help when you need it.
There may not be a cure, but there is hope as you take ownership of your healthcare and work with your provider on finding treatments that help decrease your most difficult symptoms. It takes time and diligence, but it’s possible to increase the number of good hours, days, weeks, and years.





























15 Responses
This web site is very informative and i have seen alot of my symptoms in the list here. I am seeing a PC who suspects dysautonomia for many reasons and I am wondering how do you find a practitioner that understands dysautonomia and can diagnose/treat me. Thank you for your help in advance.
Sincerely, Diane Bolton
Not sure, I see a cardiologist, I haven’t been diagnosed yet but I think I have this. I was brought in to hospital by ambulance because my heart stops for up 30 seconds at a time for no apparent reason, this the cardiologist. So maybe a cardiologist if you have heart issues or a neurologist would be the best bet I think.
Hi! I read through this post and it reminds me of my old roommate who would always talk about similar topics. I will definitely forward this to him. Thank you for sharing!
Hi I was wondering if anyone could mention a few MDs who take out of pocket patients, this is difficult to manage. thanks.
Thanks also to Diane Bolton for sharing her experience, would you be able to mention your Dr? It may be helpful if he/she knew of other Drs who are versed well in dysautonomia. thanks in advance
Dee
This post was truly remarkable, especially because I was looking for thoughts on this issue last Thursday.
Someone HELP!!! I have seen multiple doctors. No one has a clue. Waited 6 months to see a Neuro specialist. He did a tilt table test, catecholimine test and a breathing test. I was told everything was normal. He didn’t care about my freezing or burning up episodes, my palpitations, my esophageal spasms, (that my GI doctor insisted I tell him about). The change in my bowel and bladder patterns. I could go on and on. He made me feel crazy. He informed me if I feel bad still in a year. A YEAR to come back and see him. I need help. Where to turn.
I have been through the western medicine ringer too. I have been seeing specialist since I was born and have gotten a million different diagnoses, all of which has no solution except for drink more water and increase your salt intake. This all changed for me when i saw this neurologist at ucdavis. He explained my condition beautifully. He said that I had dysautonomia and that this basically means there is a lag between your brain and your body. Your brain and your body could work fine but there is an unknown disconnect between the two systems which causes a wide range of symptoms. Because of this, my body cannot stay at homeostasis and can’t function properly. I know this will be hard to hear but there isn’t a clear solution. For me, hearing what that doctor had to say really changed my perspective on life. He said that to help minimize the symptoms, I need to recondition myself. This means trying to eat right and exercise more. This may seem so out of reach and ridiculous but it does help. What helps even more is being spiritually stable even if everything else in the world or in your body isn’t. Having strong faith, being in nature, finding the light in life, along with finding those people to be there for you is completely life changing. Doctors, for the most part, are so frustrating; going in and out of specialist offices, being told you are “completely fine” or “normal” is so infuriating when you know something isn’t right. I would say, Susan, that you can continue to look for answers, but being able to live your life no matter what health crap you are going through is the most important thing to keep in mind. I am so sorry for what you are going through but not letting this define you is so important so I want to say that there is hope within all of the darkness you may see. I Hope this gives you a little hope!
Ask your family physician (gp) to find you a movement disorder specialist
Where do you live? I know an amazing doctor here in Alabama if you are willing to make the trip to see him. He is well educated in dysautonomia. I, like you, experience more of the issues associated with my GI system. I saw
9 different GI doctors that all diagnosed me with something different before I did loads of research on my own and decided this had to be neurological since I have Gastroparesis and that involves
Damage to your vagus nerve! I was right. The vagus nerve is a key part of your autonomic Nervous system. I was sent to a dysautonomia specialist in Birmingham and I scored 2 points too low on my testing so they denied me a diagnosis even though my symptoms are all present and severe. I was devastated but my neurologist knew better. When I returned to him he denied the Specialists recommendation and gave me the official diagnosis of FAMILIAL DYSAUTONOMIA because it is the main one that affects your GI system and other issues i have and am experiencing. Such as not being able to produce tears at birth. I am still fighting the management of symptoms as it takes an army of different doctors to support all of your symptoms but HAVING AN OFFICIAL DIAGNOSIS ON RECORD HELPS!! Doctors start believing you and since their education and understanding of dysautonomia is limited, they acrually start listening to your requests as they do not have the time to research it themselves. Getting at at home iv therapist twice a week to give me lactated ringers which contains electrolytes to help keep me hydrated since drinking over the recommend amount alone doesnt help because i dont absorb nutrients properly. It helps in so many ways but mainly in having a little more energy and being able to go to the bathroom. Going to a GI doctor and pleading for a Gastritic stimulator is now my next victory! He listened to me, saw my previous 9 years of testing history and my diagnosis from my neurologist and has referred me back go Birmingham at UAB to see a surgeon to have a gastric stimulator placed in my body. I know there is probably going to be more recent repeated testing required for insurance purposes before the procedure is permitted but it is a start for a hope for my future. My next step is going to be to ask for an iv port and to increase my iv fluids to twice a day and to find a way to have the medications I take and the nutrients I am lacking given interveniously since I have a hard time digesting and absorbing things. My medications all reach me at about half strength at best. Sometimes not at all. Sometimes, even though taken separately and at several hour apart increments, they hit me all at once causing major issues and side effects. I have a huge list of side effects and symptoms associated with this disease. I have a probable secondary diagnosis of multiple sclerosis due to MRI results not only showing several white matter lesions on my brain but a lesion on the t-9 portion of my spine showing a Dymelantating disease that is consistent with an MS diagnosis. Along with that I have just developed masses on my right kidney and one of them is complex with fatty component- which I just now learned through a rabbit hole of research- that is directly connected to the t-9 portion of your spine. It is very painful. In fact, dysautonomia causes me very severe pain. The biggest pain that I have is what is called “the MS hug” but people with dysautonomia can also experience it. I see a pain doctor who is also a wellness doctor. He is compassionate and also, like my neurologist, actually listens to me. My fiance just paid out of pocket for two tests for me, that my pain/wellness doctor wanted me to get. They were both $800 a piece. One of them is called a GI Map from diagnostic solutions. I had to bring home a kit to mail off a stool sample. Among other things, It is going to give an accurate picture of my gut biome to help get insight on what needs work to help find relief and possible repair. I don’t remember what the other test was but it required blood work to be done. The neurologist that I see is Dr. Laganke in Cullman, Alabama and I also see Dr. Thacker in Huntsville, which is my pain/wellness doctor. One thing I will note, I did pay out of pocket ($450 each time) for two rounds of testosterone treatments- since my blood testing showed that I was low- and females apparently need an adequate amount of testosterone ourselves. However, this has proven to only exasperate my dysautonomia symptoms and has made my temperature Intolerance almost unbearable, especially to heat, along with the temperature dysregulation ni also grew a mustache and a few hairs on my chin and became quite aggressive. So I hope this helps someone else not waste their time or money. However, everyone is different, so what helps me may not help everyone. I have a lot more information I can share but Hypersomnia calls my name for now as I can barely stay awake trying to type this out! Hope this helps someone. Feel free to reach out to me at Djentress@gmail.com or laciemalia@gmail.com.
Have you checked your thyroid labs? It is important to rule that out. Often there can be multiple issues.
Despite a long history of education and practice in the medical field, this article was so clear and concise, so thorough, so informative that I now have a better understanding of all aspects covered.
If anyone is looking for a doctor with a dysautonomia specialty, please indicate from where you come.
Best to all.
Dr Ramesh Adjira Bristol pa best dr for autonomic dysfunction helped me so much
I have recently learned I have DBH deficiency through multiple genetic tests. This explains symptoms I have been experiencing for as long as I can remember. I’m so glad to have found your website. Thank you for the resources and support.
i really think I do have this
I have dysautonomia with hypotension,bradycardia and vasovagal syncope from baroreflex failure due to stress and chronic PTSD I’ve had to stop work due to flare ups and had to go through HR meeting where I’ve been called lazy and faking fainting and lying about how low my blood pressure is to the point I’ve had to show them my medical records to prove I have this condition even my husband didn’t believe it until we got a blood pressure machine at home took reading four times a day and he saw how low reading Were I’m really glad that I’ve read this to prove that I’m not alone and this is real I just wish more people understood this condition and there was more information available